
3dcombine 405 Free Download
Aug 8, 2016 - Many properties of brain function are associated with scale-free. Microsoft powerpoint slides free download. Sustained Attention to Response Task (SART), 405 (±83), 423 (±83), 93.7. With an isotropic 6 mm Gaussian kernel with AFNI 3dmerge. Download article.
Windows 7 Download periodically updates pricing and information of 3DCombine free download from the publisher, but some information may be out-of-date. Using cracks, warez serial numbers, registration codes or keygens for 3DCombine license key is illegal. Free download links are directly from our mirrors or publisher's website, 3DCombine torrent or shared uploads from free file sharing and free upload services, including MegaUpload, Rapidshare, HellShare, HotFile, FileServe, YouSendIt, DepositFiles, SendSpace, DivShare or MediaFire, are not used.
Depressive symptoms often coexist with memory deficits in older adults and also are associated with incident cognitive decline in the elderly. However, little is known about the neural correlates of the association between depressive symptoms and memory deficits in nondemented elderly. Fifteen amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and 20 cognitively normal (CN) subjects completed resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (R-fMRI) scans. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to test the main effects of the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) and Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test delayed recall (RAVLT-DR) scores, and their interaction on the intrinsic amygdala functional connectivity (AFC) network activity. Severer depressive symptoms and memory deficits were found in the aMCI group than in the CN group. Partial correlation analysis identified that the RAVLT-DR scores were significantly correlated with the AFC network in the bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), dorsomedial and anterior prefrontal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex (PCC), middle occipital gyrus, right inferior parietal cortex, and left middle temporal gyrus (MTG).
The GDS scores were positively correlated with the AFC network in the bilateral PCC and MTG, and left DLPFC. The interactive effects of the GDS and RAVLT-DR scores on the AFC network were seen in the bilateral PCC, MTG, and left DLPFC. These findings not only supported that there were interactive neural links between depressive symptoms and memory functions in nondemented elderly at the system level, but also demonstrated that R-fMRI has advantages in investigating the interactive nature of different neural networks involved in complex functions, such as emotion and cognition. Introduction Several clinical and epidemiologic studies have demonstrated that depressive symptoms and memory deficits often coexist in late life (;;; ). It has been reported that depressive symptoms are highly prevalent in subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), and the presence of mood symptoms increases the risk of progression from aMCI to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (;;;; ). Similarly, the presence of cognitive deficits in patients with late-life depression is associated with future incidence of AD (; ).
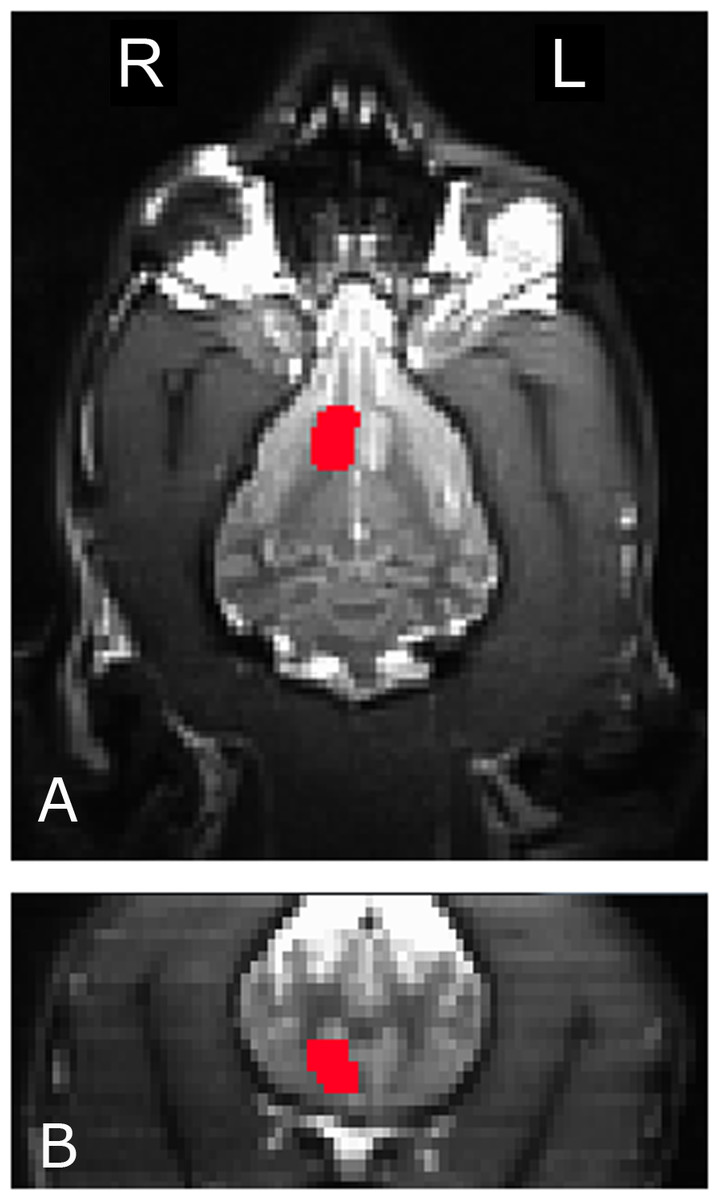
The co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and memory deficits increases the risk of subsequent cognitive decline and incident AD in nondemented older adults. Recently, advances in the development and application of imaging approaches and network analyses have made it possible to investigate the underlying mechanisms of the complex relationship between depressive symptoms and memory deficits, and to study how these two behaviors are linked or interacting at the neural network level. Previous studies have employed task-driven functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) experiments to investigate the functional localizations related to depression and cognition (;;;; ).